Decoding Seborrheic Dermatitis: Identifying Symptoms for Proactive Management
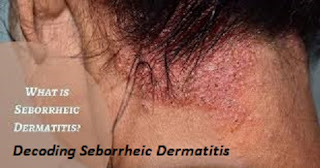
Seborrheic dermatitis is the most common inflammatory skin condition, which presents as scaly patches and red skin on the oily areas of the body, such as the scalp, face, sides of the nose, eyebrows, ears, eyelids, and chest. Usually, this condition fades away on its own in infants and some adults. If the symptoms don’t subside, there are many effective proactive strategies mentioned below to manage the symptoms and to stop seborrheic dermatitis from flaring up in the future. Prevalence and Etiology Seborrheic dermatitis is most commonly seen in infants and adults between 30 and 60, but it can affect people of any age. Studies say that 3–10 people in every 100-experience seborrheic dermatitis during their lifetime. Seborrheic dermatitis is not a contagious infection, meaning you can’t get it from another person. Usually, it is due to certain genetic and environmental factors that trigger the condition. Common factors that cause seborrheic dermatitis include: Stress Hormonal chang...